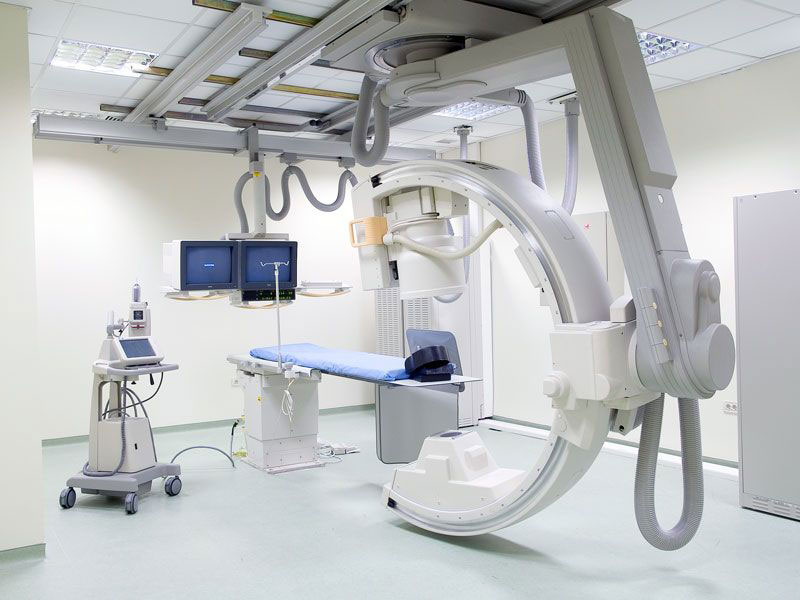
Hemodynamic Laboratory
The Hemodynamic Interventions laboratory is one of the most advanced medical departments. The correct diagnosis of each cardiovascular disease is made in this lab as well as the decisions on the type of treatment (conservative or surgical) that needs to be applied.
Angioplasty of the coronary arteries, sometimes called a balloon, or PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention), is a treatment performed by specialized invasive cardiologists to open the blocked coronary artery and restore blood flow to the myocardium.
Angioplasty is used as an alternative procedure in bypass surgery. Coronary artery angioplasty is performed on an emergency basis to treat chronic coronary stenosis and also on urgent basis to treat acute myocardial infarction, for which is the most effective treatment, significantly reducing patient mortality compared to simple medication.
Some people, while suffering from heart disease, have no symptoms or have misleading discomfort (eg, pain in the shoulder or abdomen). This is especially true for the diabetics and the elderly. So they either not go to a doctor at all or when they go and report their symptoms, the mind of the physician is not directed to a cardiac condition.
Another problem is that non-invasive cardiac tests are not always correct. There is a lot of important information left out, which is not only related to the imperfection of the diagnostic machines, but also to the health condition of the examinee.
The Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty are the only diagnostic methods with 100% accuracy for the diagnosis but also with a simultaneous treatment of the coronary heart disease.
How angioplasty with stent placement is performed:
The doctor inserts a catheter (called angioplasty catheter guide), 2-3 mm in diameter, into a large peripheral artery, which leads to the mouth of the narrowed artery of the heart. The catheter is driven by the femoral artery in the same way that the coronary catheter is guided.
Then, through the catheter, he inserts a long and very thin wire (called a guide wire for angioplasty) which reaches and passes through the narrowing of the artery. On this wire "rolls" a catheter that has a balloon at the end, which is placed inside the stenosis. The doctor then inflates the balloon, which compresses the atherosclerotic plaque and dilates the narrowed artery. The balloon catheter is then removed.
If the doctor decides to place a stent, then over the guide wire "rolls", another catheter that brings to the edge of the balloon outside which the stent is placed.
As the balloon inflates, the stent expands and stabilizes in the vessel walls. The balloon is then deflated and removed while the stent remains in the stenosis, keeping the artery open eliminating the stenosis while avoiding the stenosis of the vessel.
Stents with drug release
If cardiology uses the human circulatory system as a "national route" to implement a treatment with various devices, it could also use it to administer a drug locally. Thus, stents that locally release various drugs, that were known to interrupt the biological processes that cause restenosis, are used. The stents were "dressed" with these drugs, which were adapted to a thin polymer layer on the outside of the stent and are characterized by three elements.
- The type of stent that bears the drug
- The way the drug is released
- The type of drug released and how it acts on the arterial wall to prevent re-stenosis
The choice of stent size, type and layout is made during coronary angiography, in the catheterization laboratory.
At the “OLYMPION” General Clinic, top quality stents are provided, by leading companies in Europe and the USA, exclusively for Patra.
The whole range of Angioplasty procedures is carried out with equipment of the latest generation, in a comfortable and modern environment.
The General Clinic is contracted with EOPYY, while it also maintains collaborations with the most well-known private insurance companies.
Recognize the symptoms and prevent the heart attack
The Hemodynamic Laboratory is an integral part of the Cardiology Clinic.






